

- #LINEAR REGRESSION VEUSZ MANUAL#
- #LINEAR REGRESSION VEUSZ CODE#
- #LINEAR REGRESSION VEUSZ PROFESSIONAL#
#LINEAR REGRESSION VEUSZ CODE#
For instance, this piece of code constructs a simple x-squared plot which changes to x-cubed (it is referenced from the official documentation): import veusz.embed as veusz import time # open a new window and return a new Embedded object embed = veusz.Embedded('window title') # make a new page, but adding a page widget to the root widget page = ('page') # add a new graph widget to the page graph = page.Add('graph') # add a function widget to the graph. There is, therefore, another competitor to the standard python libraries such as Matpotlib, Seaborn, or Plotly. Veusz can be used as a Python module for plotting data. The NumPy package is already imported into the command line interface. Veusz can also read Python scripts from files. When commands enter in the command prompt in the Veusz window, it supports a simplified command syntax, where brackets following commands names can be replaced by spaces in Veusz commands. Therefore you can freely mix Veusz and Python commands on the command line. As Veusz is programmed in Python, it uses Python as its scripting language. Command-line interfaceĪn alternative way to control Veusz is via its command-line interface. Properties of widgets are edited in the Properties window, and their appearance and formal side (font, axis line color, color of labels, etc.) in the Formatting window. In Veusz, plots are created by building up plotting widgets, specific elements (charts, axes, text labels, etc.) that the user adds or removes in the Editing window.
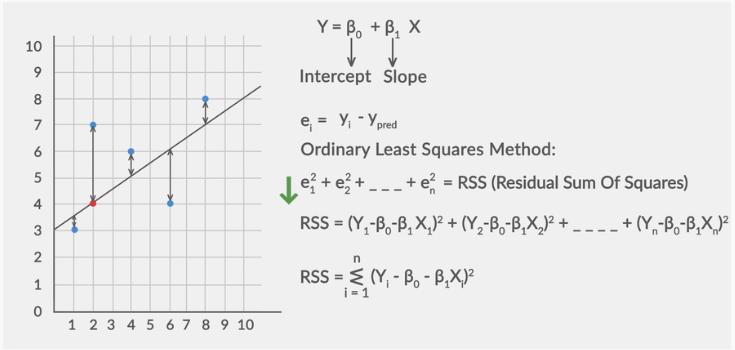
#LINEAR REGRESSION VEUSZ MANUAL#
Manual formatting involves importing data and manual editing graphs to build the 2D or 3D product. Veusz allows formatting graphs in three ways:

#LINEAR REGRESSION VEUSZ PROFESSIONAL#
linregress ( t, xn ) print ( 'Linear regression using stats.linregress' ) print ( 'parameters: a= %.2f b= %.2f \n regression: a= %.2f b= %.2f, std error= %.3f ' % ( a, b, a_s, b_s, stderr )) print ( ' \n ' ) # matplotlib ploting title ( 'Linear Regression Example' ) plot ( t, x, 'g.-' ) plot ( t, xn, 'k.' ) plot ( t, xr, 'r.Veusz is a graphing program designed to produce publication-ready plots for academic and professional journals. From scipy import linspace, polyval, polyfit, sqrt, stats, randn from matplotlib.pyplot import plot, title, show, legend # Linear regression example # This is a very simple example of using two scipy tools # for linear regression, polyfit and stats.linregress # Sample data creation # number of points n = 50 t = linspace ( - 5, 5, n ) # parameters a = 0.8 b = - 4 x = polyval (, t ) # add some noise xn = x + randn ( n ) # Linear regressison -polyfit - polyfit can be used other orders polys ( ar, br ) = polyfit ( t, xn, 1 ) xr = polyval (, t ) # compute the mean square error err = sqrt ( sum (( xr - xn ) ** 2 ) / n ) print ( 'Linear regression using polyfit' ) print ( 'parameters: a= %.2f b= %.2f \n regression: a= %.2f b= %.2f, ms error= %.3f ' % ( a, b, ar, br, err )) print ( ' \n ' ) # Linear regression using stats.linregress ( a_s, b_s, r, tt, stderr ) = stats.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
